Back
Lesson 25:
Transacting Ether
Introduction to transacting ether in your smart contracts.
Progress: 0%
Visit desktop version for better experiences.
Transacting Ether
Ether transactions comprises of two main parts: sending and receiving ether.
Recall that methods to transact ether revolves around payable keyword.
Sending Ether
transfer/send(NOT recommended due to 2300 gas limitations allowing potential reeentrancy attacks)sendValueOpenZeppelincall
Recommended method is using call paired with reentrancy guard.
Simple example of sending Ether using call method:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.24;
contract SendEther {
address public sender;
uint256 public amount;
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
function sendViaCall(address payable _to) public payable {
// Remember to update the balance before interactions prevent reentrancy attacks!
// Follow Checks-Effects-Interactions pattern
balances[msg.sender] -= amount;
balances[to] += amount;
// Call returns a boolean value indicating success or failure.
// This is the current recommended method to use.
(bool sent, bytes memory data) = _to.call{value: msg.value}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
}
}Using ReentrancyGuard:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.24;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/ReentrancyGuard.sol";
contract SendEtherExample is ReentrancyGuard {
constructor () ReentrancyGuard() {}
// Event to emit when Ether is sent
event EtherSent(address indexed to, uint256 amount);
// Function to send Ether using the `call` method
function sendEther(address payable recipient, uint256 amount) external payable nonReentrant {
// Check that the contract has enough Ether to send
require(address(this).balance >= amount, "Not enough Ether to send");
emit EtherSent(recipient, amount);
// Send the Ether and check that the call was successful
(bool success, ) = recipient.call{value: amount}("");
require(success, "Failed to send Ether");
}
// Function to check the contract's Ether balance
function getBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}If sending Ether after an effect, The recommended method to send Ether after an effect is using the withdrawal pattern.
Receiving Ether
Recall payable keyword when implementing an Ether receive function.
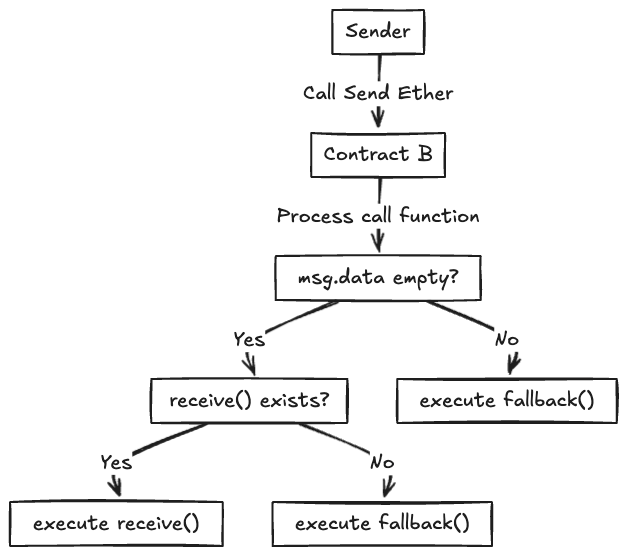
If a contract receives Ether (without a function being called), either the receive() external payable {...} or the fallback function is executed.
Ether will be rejected (by throwing an exception) if there are no receive or fallback functions.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.24;
contract ReceiveEtherExample {
// Event to emit when Ether is received
event EtherReceived(address indexed from, uint256 amount);
// Function to receive Ether
receive() external payable {
emit EtherReceived(msg.sender, msg.value);
}
// Fallback function
fallback() external payable {
// This function is called when no other function matches the called function,
// or when someone just sent Ether without calling a function
emit EtherReceived(msg.sender, msg.value);
}
// Function to check the contract's Ether balance
function getBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}Flowchart to determine fallback or receive:
FallbackEnd of lessons